Fabrication of Ternary Metallic Membranes for Neutral-Carbon Hydrogen Production through Water Gas Shift Reaction
To limit global warming, the conventional industrial energy system must be decarbonized urgently. One potential solution is hydrogen (H2) gas, which is considered the energy carrier of the future due to its high energy density compared to hydrocarbon fuels and zero-carbon emissions.
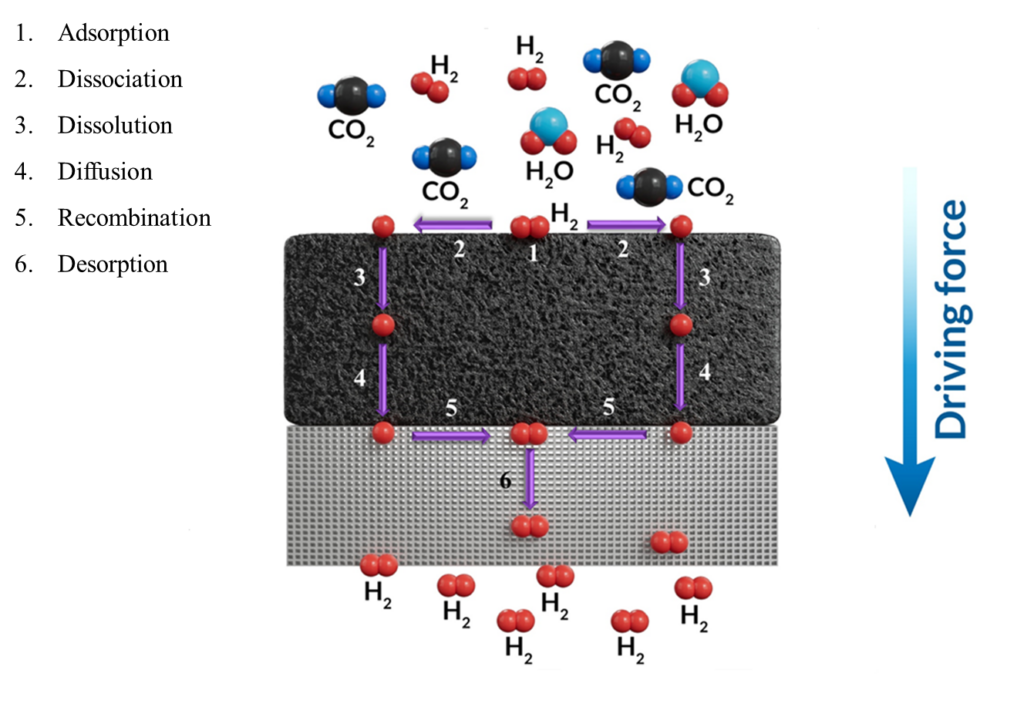
Metallic membrane reactors (MRs) are a promising technology for generating neutral-carbon hydrogen from water gas shift reaction (WGS). Unlike the conventional separation techniques, which require additional and energy-intensive steps, metallic MRs show high selectivity toward hydrogen and good efficiency.
Ternary Pd-alloy membranes will be fabricated using the electroless plating (ELP) technique, which requires less energy, is low-cost, and covers complex geometry.
Mineral Separation and Recovery by Surface Functionalized Polymeric Membrane
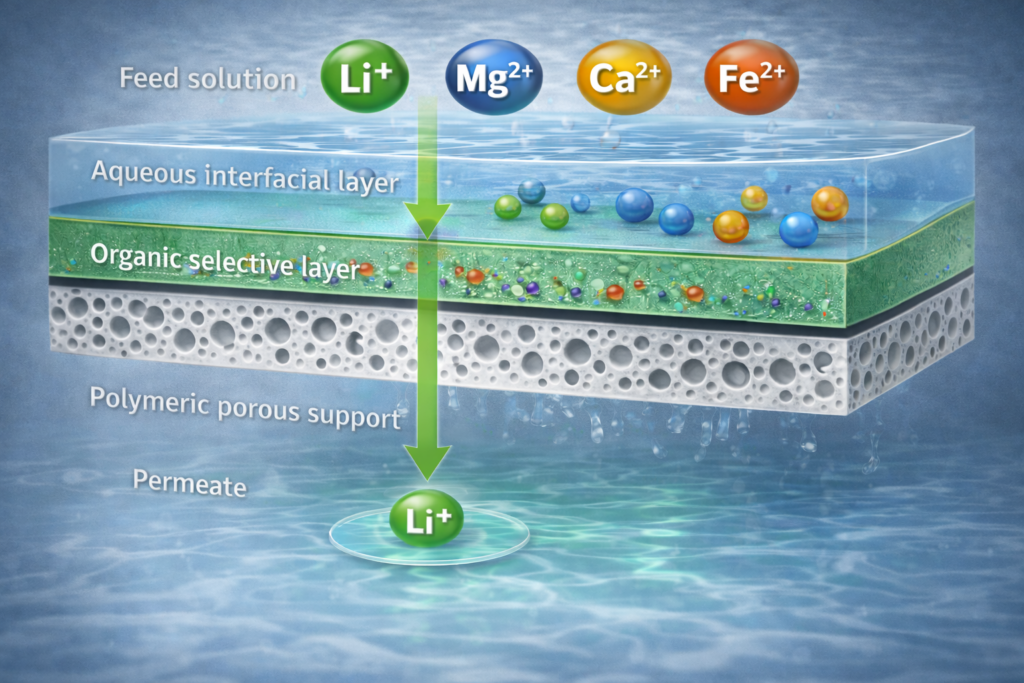
Surface-functionalized polymeric membranes have emerged as a highly effective platform for the selective separation and recovery of monovalent and divalent ions from complex aqueous streams. By tailoring the membrane surface chemistry through the incorporation of charged functional groups, ion selectivity can be precisely controlled via a combination of Donnan exclusion, electrostatic interactions, and size-sieving effects. Positively or negatively charged moieties introduced onto the membrane surface enable preferential rejection of multivalent ions while allowing targeted permeation of monovalent species, or vice versa, depending on the functionalization strategy. This tunable selectivity is particularly advantageous for mineral recovery applications, where efficient separation of ions such as Li+, Na+, Mg2+, and Ca2+ is critical. Compared to conventional separation processes, surface-functionalized polymeric membranes offer lower energy consumption, modular scalability, and enhanced chemical stability, making them well suited for sustainable recovery of critical and strategic minerals from dilute and high-salinity feed streams.
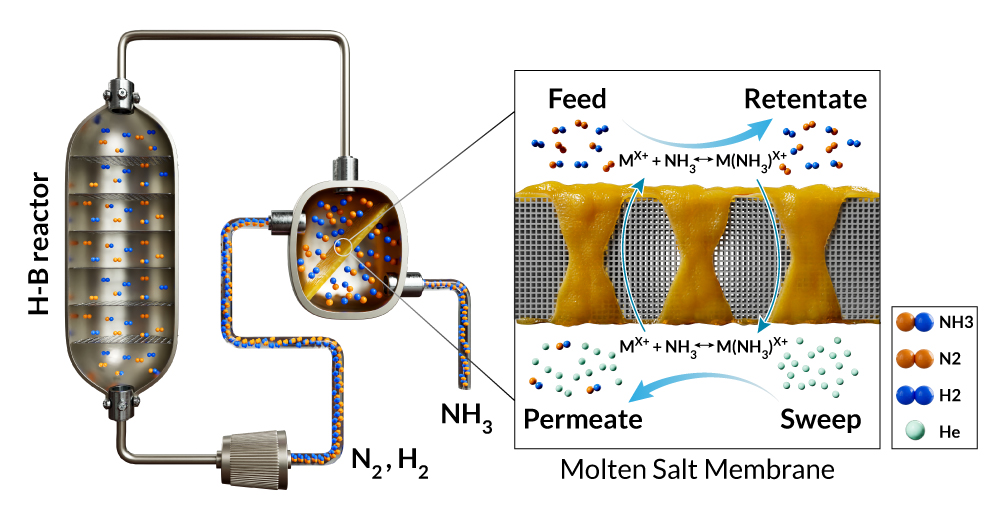
Ammonia Separation with Molten Salt Membrane
A chain of heat exchangers and a final refrigeration stage are usually used to recover ammonia in industrial Haber-Bosch (H-B) process, while the unreacted hydrogen and nitrogen are reheated and recycled to a catalytic converter using compressors. Membrane technology provides a promising alternative to intensify the H-B process by using ammonia–selective membranes. The ammonia–selective membranes must be heat resistant and possess separation characteristics of high permeability and selectivity. Molten salt membrane could be a promising membrane to recover ammonia, thus reducing the carbon footprint and energy consumption of Haber-Bosch process.
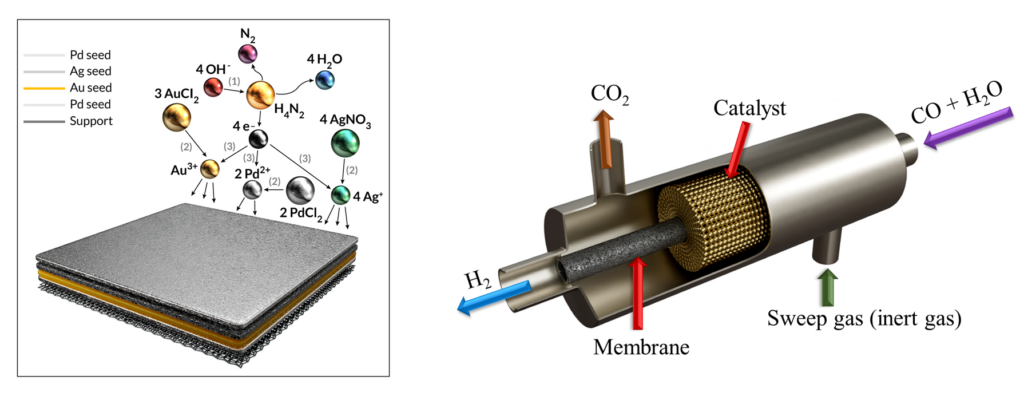
Hydrogen Production and Separation by Pd-based Membrane Reactor
Currently, hydrogen is mainly produced by natural gas steam reforming in conventional reactor which required high operating conditions and several step and purification, thus it cause emission 9-12 kg of CO2/Kg of H2. The membrane reactors allows to separate hydrogen from the reaction simultaneously. This feature help to shift the reaction towards consumption of reactants so higher conversion achieved at lower temperature. Moreover, there is no need for separate purification unit with membrane reactor so it reduce required space and units for hydrogen production and separation.